AGL dives deeper into coal – have renewables lost a friend?
The utility that once prided itself on being the cleanest in Australia, and insisted that the best way to prepare for a clean energy future was to invest in renewables, is proposing to dig itself deeper into coal.
AGL Energy on Wednesday announced it had won the bidding for Macquarie Generation – the largest coal generator in NSW – for the knock down price of $1.5 billion. Like its 2012 purchase of Loy Yang A, the biggest brown coal generator in the country, AGL has found itself in the right place at the right time. It’s no doubt terrific news for shareholders, the bigger question is what it means for the future of renewable energy in this country.
 AGL has been one utility in the country that has not had an antagonistic attitude towards wind energy and solar. It has supported the renewable energy target, and it chairs the Clean Energy Council, and has been the biggest individual investor in wind and solar farms. Its presentation for the MacGen purchase even begins with a picture of clean running water.
AGL has been one utility in the country that has not had an antagonistic attitude towards wind energy and solar. It has supported the renewable energy target, and it chairs the Clean Energy Council, and has been the biggest individual investor in wind and solar farms. Its presentation for the MacGen purchase even begins with a picture of clean running water.
Now, however, if the purchase of the 2.6GW Bayswater and 2GW Liddell coal-fired generators in the Hunter Valley are approved, its leverage to fossil fuel income over renewables will jump from around 7:1 to 12:1, analysts say. The company that once had an emissions intensity (0.36t/MWh) – little more than one third the country’s average – will now have one of the highest.
The proposed purchase will come under scrutiny from the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC), which has already flagged its concerns about AGL owning more than one quarter of generation in three key states – NSW, Victoria and South Australia, and being in a position to control market prices.
But there are broader questions for the renewable energy industry in this country is whether AGL will remain as staunch a supporter of green energy and the rapid transition to a low carbon economy as it has been in the past. It is hard to imagine given it is moving quickly in the opposite direction.
AGL wasn’t commenting over and above its media statement today. At the time of the Loy Yang A purchase (another knock-down price), CEO Michael Fraser insisted the company had not “changed its stripes” and it was a good thing that it could us “coal cash” to invest in renewables.
But now that it proposes to further increase its leverage to fossil fuels, and become the largest coal-fired generator in the country, exactly how supportive of renewable will it be.
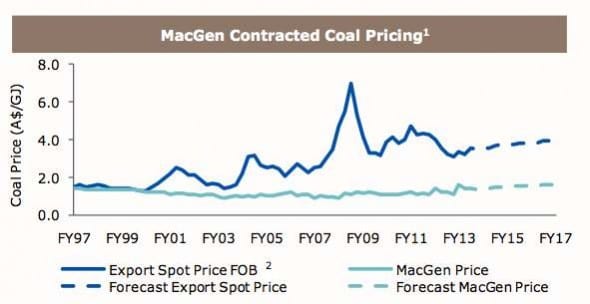 The real attraction of the purchase is that MacGen can source its coal so cheaply it can get its money back from the purchase in just 7 years. Thanks to historic contracts, the coal it uses (more than 10 million tonnes a year) is literally shoveled on to conveyor belts at an average cost of just $34/tonne – that is less than one half of the price that those same mines receive for exported coal.
The real attraction of the purchase is that MacGen can source its coal so cheaply it can get its money back from the purchase in just 7 years. Thanks to historic contracts, the coal it uses (more than 10 million tonnes a year) is literally shoveled on to conveyor belts at an average cost of just $34/tonne – that is less than one half of the price that those same mines receive for exported coal.
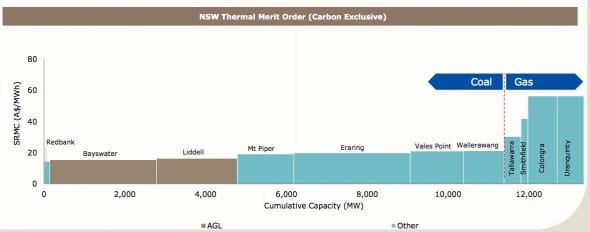
Even with a predicted 25 per cent increase in those coal contracts in coming years, MacGen will still sit – as Loy Yang A does in Victoria – at the bottom of the “merit order” for thermal generators in the two states.
That should mean that AGL is better protected from some of the seismic shifts that are sweeping the electricity industry, and which have forced more expensive coal-fired generators such as Tarong, Collinsville, Playford and, imminently, Wallerawang, to be closed or mothballed.
It should be noted that Liddell is old and creaking and will possibly be closed well before its due to retirement date of 2022. Last year, because of “availability issues” it had a net capacity factor of just 35 per cent. That hardly makes it baseload – most Australian wind farms – including AGL’s have higher capacity factors.
Still, AGL has now nearly doubled its exposure to the threat of declining demand and the impact of distributed generation – the arrival of rooftop solar and the potential addition of battery storage. Even if the purchase is priced that it can get its money back quickly, those revenue streams will be worth protecting.
AGL has defended the renewable energy target – and lambasted those who sought to pull it down: Its chairmanship of the CEC would hardly permit it to do anything else.
But its submission to the energy white paper is informative, and suggests its priorities are shifting. It argues strongly for policies in the gas market, and for deregulation of the retail market, but does not argue a particular position on the RET.
Instead, AGL adopts the language used by other generators and utilities who argued specifically for the RET to be either dumped altogether, or severely diluted. It warns against the decline in demand, worsened by the influx of renewables, that is causing wholesale electricity pool clearing price to be “sub-economic”.
AGL wants the gap between the wholesale price addressed, either through some form of capacity payments to keep plant open, and/or a mechanism that helps ageing and/or inefficient plants to exit the market permanently.
At no point does it argue specifically for the RET target to be retained as is. It says this:
“The decline in demand has also contributed to the existence of surplus generation capacity, particularly a surplus of baseload capacity. The Renewable Energy Target was designed with a view that new renewable investment would be required to meet increased electricity demand.
“As demand declined but supply continued to be added, this led to the market becoming oversupplied, with the consequence that current wholesale electricity prices (and a declining real penalty price for LGCs) are unlikely to support new investment in renewable generation.”
“Accordingly, the Government’s energy reform agenda should incorporate policy measures that create a more sustainable wholesale market that facilitates new investment in an economically optimal generation mix while ensuring appropriate incentives are in place for older, less efficient plan to be withdrawn. A long-term and sustainable climate change policy framework is critical for facilitating efficient investment decisions in long-lived electricity infrastructure.”
The renewable energy industry in Australia now finds itself in an absolute pickle: Uncertainty about the RET has effectively brought investment to a halt; its strategy of negotiated compromise and its lack of ambition (can anyone name one renewable energy company which has loudly argued for a 40 per cent target by 2030, for instance) has left it little room to manoeuvre. At best, if faces a significant reduction in the target.
At worst, the industry will simply be brought to a halt. It appears certain that the RET review is to be managed by Prime Minister Tony Abbott’s office and controlled by the hard-liners who surround him and don’t even accept the science of climate change, let alone the need for wind and solar; and now its most powerful and influential facilitator is buried in the profits of coal generation.
Fraser had spent many years arguing that the best way to prepare for the carbon price was to be in clean energy. (It is sometime said that many of his fellow company executives did not share his enthusiasm for renewables). After the purchase of Loy Yang A, Fraser said the best way to prepare for the clean energy future was to be the cheapest.
Interestingly, the purchase of MacGen is predicated on there being no carbon price at all, or a market carbon price of just $7 a tonne in 2015. The European carbon price, the one that collapsed so spectacularly last year and presented Tony Abbott with a gift horse in the mouth, is now trading at $10/tonne and is certain to go higher.
AGL’s proposal looks a short-term winner for shareholders, which is what counts in the way our financial system rewards our board and executives. Time will tell whether its new strategy of fading to black is a long term gain.
Share this:


Why is there still no ability for consumers to buy their power directly from the wholesale market? This would provide lower power cost to consumers in times of low demand, and increase generator use.
Michael Fraser has said;-
“policy measures that create a more sustainable wholesale market that facilitates new investment in an economically optimal generation mix while ensuring appropriate incentives are in place for older, less efficient plan to be withdrawn”. Here’s what that means to me …
Interest in renewables is one noble thing, or noble whenever it suits, but ultimately survivability and self-interest in your business and largely your industry is holds sway over thoughts and eventually words. It goes to show the unanticipated success and popularity of solar and wind, and the ability of a negating government to change your future plan. They really did need a strict clean energy policy !
Clearly, the arrangement of wholesalers being able to balance their own investment in central generators with demand has been too comfortable. The RET and disruptive solar has diminished their coal energy business. As long as Mum & Dad are putting discretionary amounts into rooftop PV it strikes at the heart of what they do, regardless of how efficiently they do it. It’s not about about investing in clean and removing dirty. If the carbon price goes they want to keep the dirty and close the shop to a few. The purchase of Bayswater and Liddell would be the perfect hedge.